Is Plasmid DNA Quality Affecting your Transfections?
Transfection success is highly dependent upon the purity and quality of the plasmid DNA. Below are four key points to consider for ensuring successful transfections.
-
Plasmid DNA should be predominantly supercoiled and free of genomic DNA and RNA.

- Circular plasmid DNA is taken up more efficiently by the cells
- Genomic DNA or RNA contamination confounds quantification
-
Plasmid DNA should be highly concentrated and free of phenol, salts, and protein.

- Highly concentrated plasmid will not dilute transfection reagents
- Phenol will skew absorbance readings and is toxic to cells
- Salts and protein can inhibit DNA-lipid complex formation
-
Plasmid DNA should be free of Endotoxins.

- Endotoxins released during lysis can co-purify with plasmid DNA
- Endotoxins reduce transfection efficiencies and are toxic to sensitive cells
-
Plasmid DNA should be the correct sequence.
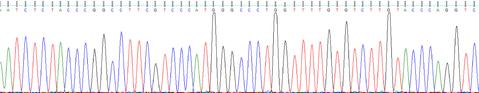
- Confirmation that the plasmid is correct is vital in achieving the objectives of the experiment.
- The performance of the plasmid DNA in these types of reactions is also a good assessment of plasmid purity and suitability for transfections.
Simplify the preparation of Transfection-Grade Plasmid DNA with ZymoPURE™

Fastest
Simple 16-minute Midi/Maxi preps
Highest Yield
Up to 25 mg from a spin-column

Ultra-Pure
Endotoxin-Free & Transfection Ready


